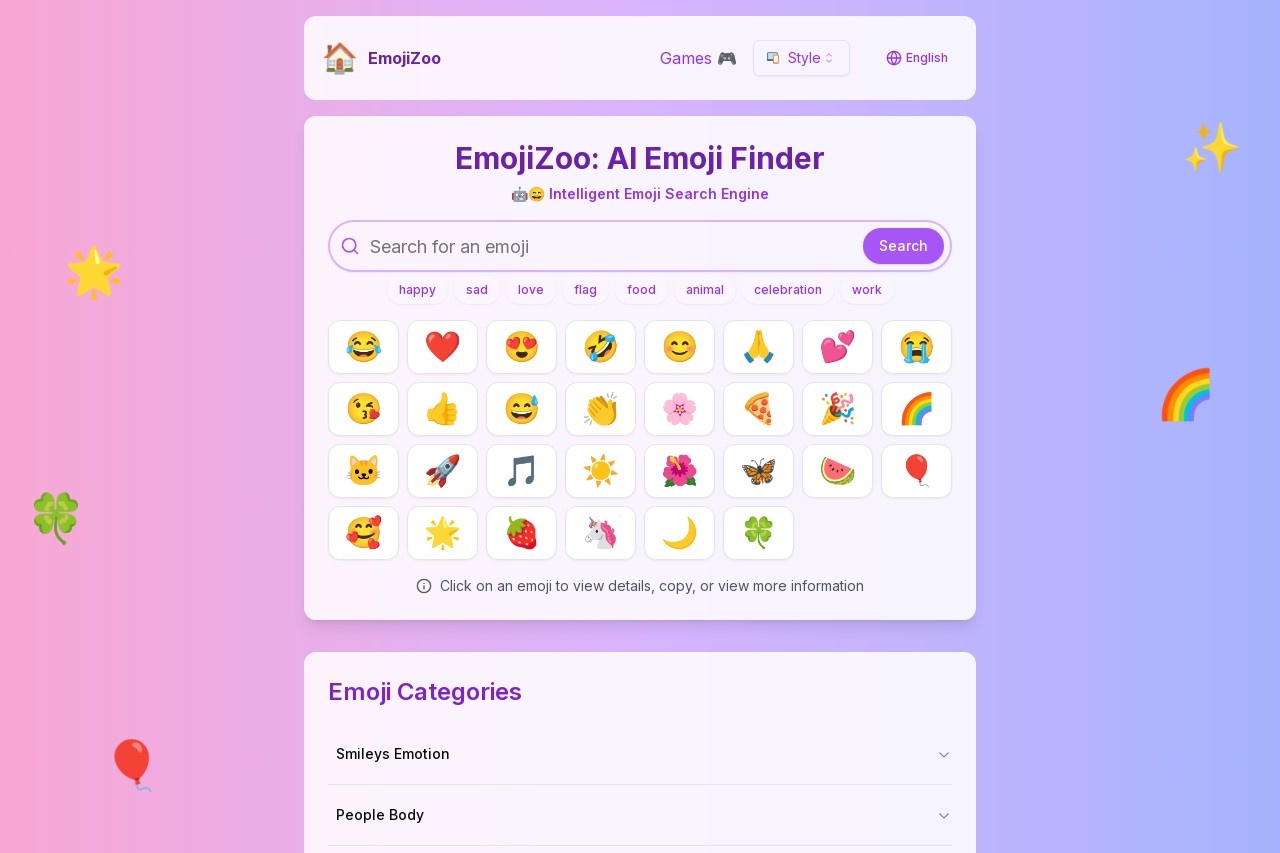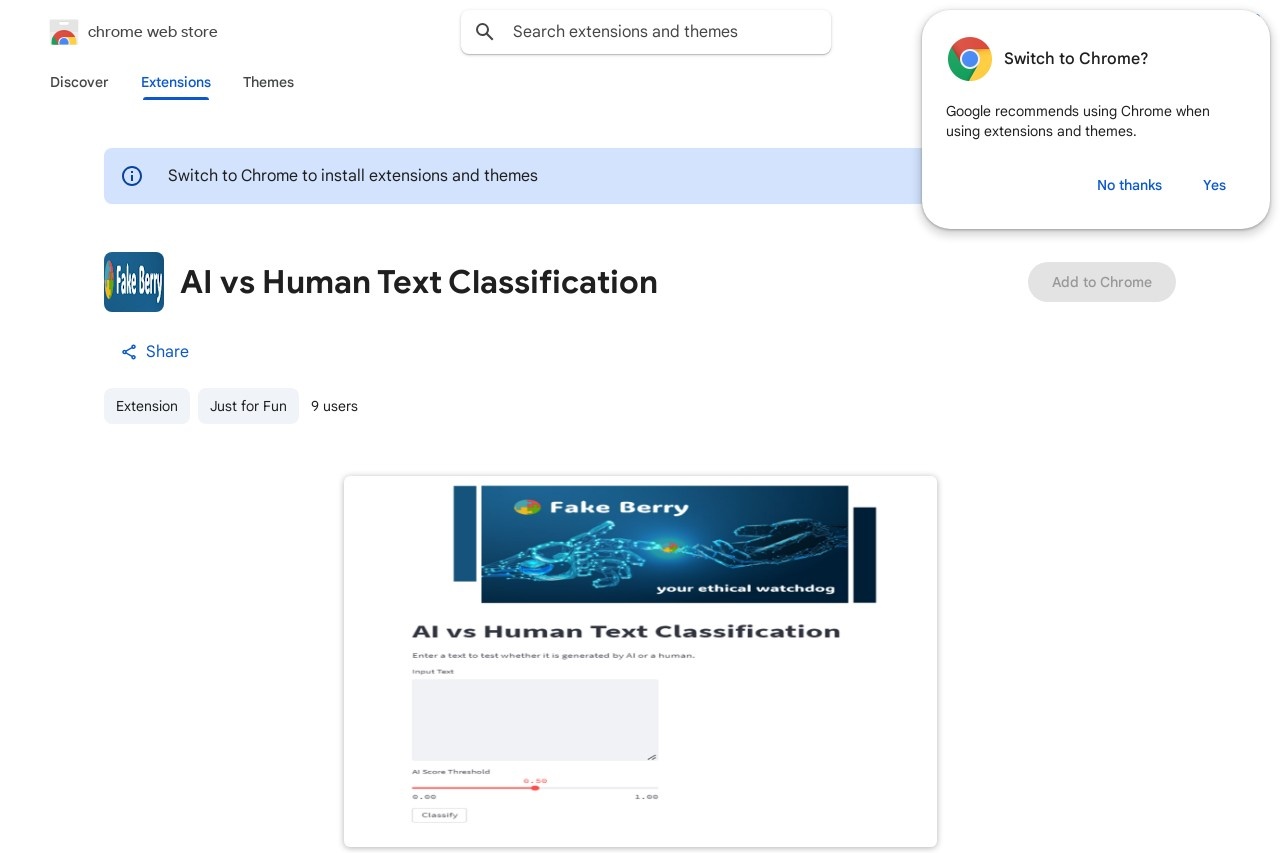
Classify text as AI or human-generated and detect toxicity.
AI vs Human Text Classification
AI vs Human Text Classification
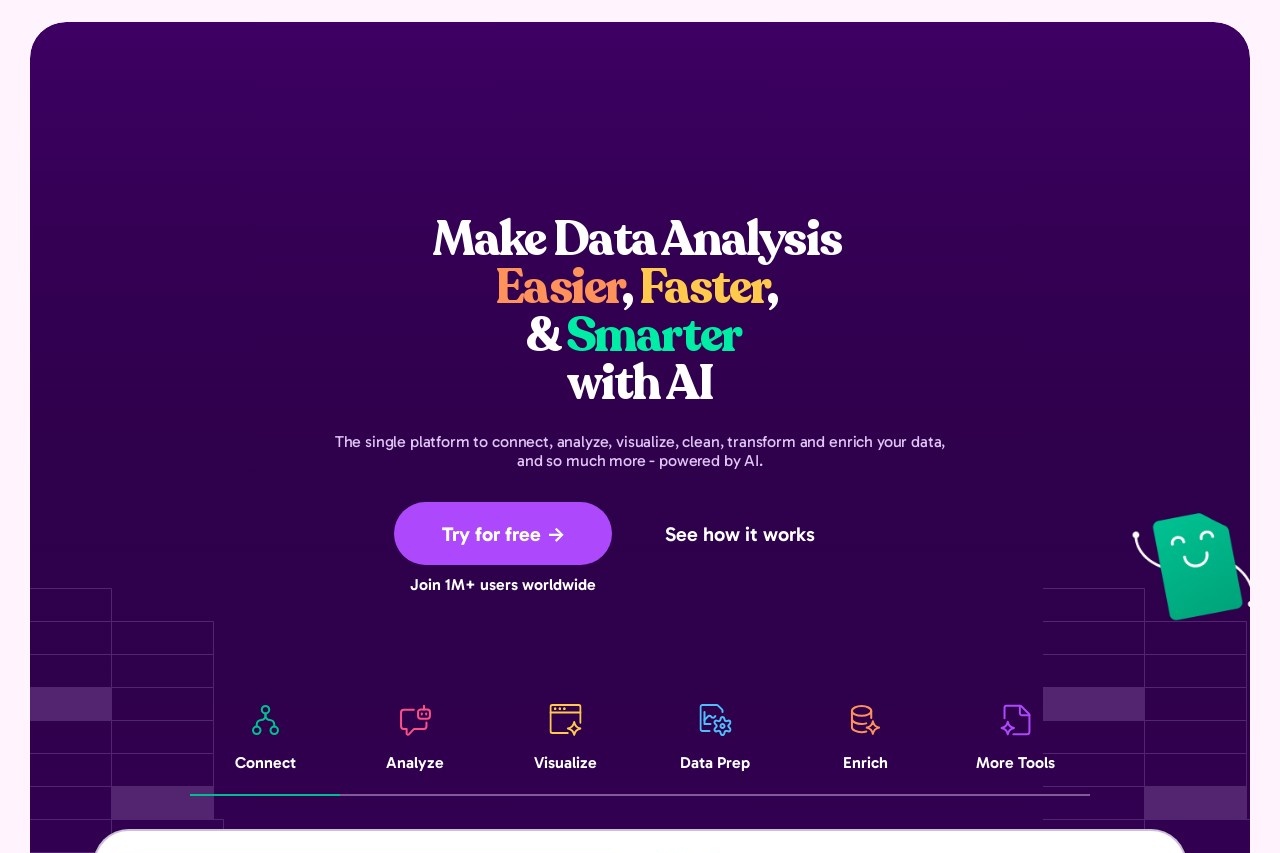
In the digital age, distinguishing between AI-generated and human-written text has become increasingly important. Whether for content moderation, academic integrity, or cybersecurity, accurate classification helps maintain trust and authenticity in online communication.
How Classification Works
Modern text classification systems analyze linguistic patterns to determine the origin of a piece of text. Key indicators include:
- Vocabulary patterns: AI models often use more predictable word choices
- Sentence structure: Human writing tends to have more varied sentence lengths
- Conceptual flow: Human authors typically show more logical progression between ideas
- Error patterns: Humans make different types of mistakes than AI systems
Toxicity Detection
Beyond origin classification, modern systems can also identify toxic content such as:
- Hate speech and discrimination
- Harassment or bullying
- Extreme profanity
- Threatening language
Advanced models use contextual understanding to distinguish between genuinely harmful content and acceptable uses of similar language.
Applications
These classification technologies serve important roles in:
- Content moderation for social media platforms
- Academic plagiarism detection
- Cybersecurity threat identification
- Market research and consumer insight analysis
- Quality control for automated content generation
Challenges and Limitations
While these systems continue to improve, current challenges include:
- AI models becoming increasingly human-like in their outputs
- Cultural and linguistic variations in human communication
- Context-dependent interpretations of toxicity
- Potential for adversarial attacks that fool detection systems
As the technology evolves, we can expect more sophisticated classification methods that better understand nuance and context while respecting privacy and ethical considerations.