Microsoft Azure
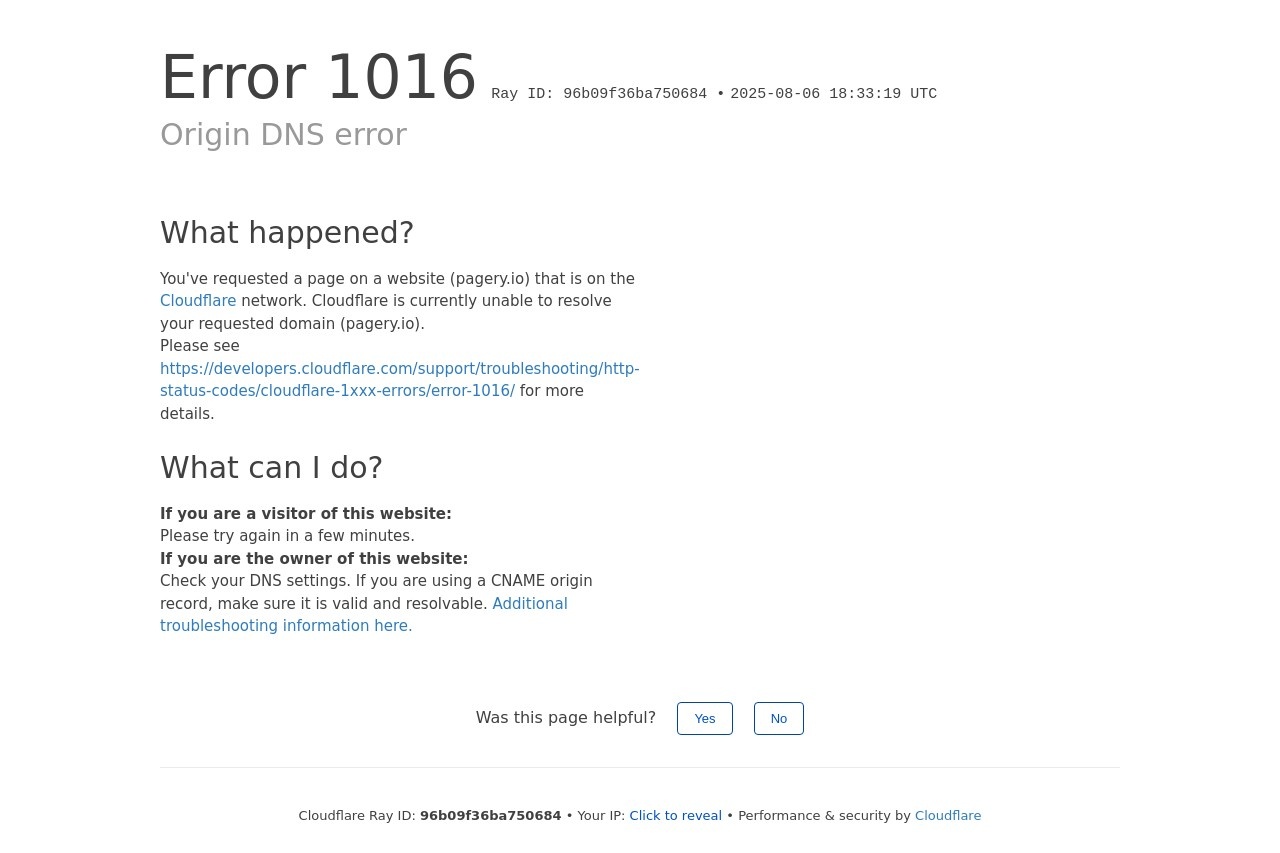
Microsoft Azure Web App Error Page for 404
When browsing a website hosted on Microsoft Azure Web Apps, you may encounter a 404 error page. This indicates that the requested resource could not be found on the server. Understanding why this happens and how to resolve it is essential for both developers and users.
Common Causes of 404 Errors
- Incorrect URL: The page may have been moved or deleted, or the URL was mistyped.
- Misconfigured Routes: The web application's routing rules may not correctly handle the requested path.
- Deployment Issues: Files might be missing or not properly deployed to the Azure Web App.
- Permissions: The requested resource may require authentication or lack proper access rights.
How to Troubleshoot
If you're a developer managing an Azure Web App, follow these steps to diagnose and fix 404 errors:
- Verify the URL and check for typos.
- Review the application's routing configuration (e.g., in ASP.NET, Node.js, or other frameworks).
- Check the deployment logs in Azure Portal to ensure all files were uploaded correctly.
- Test authentication requirements and adjust permissions if needed.
Customizing the 404 Page
Azure Web Apps allow you to create a custom 404 error page for a better user experience. Here's how:
- Create an HTML file (e.g.,
404.html) with your desired design. - Upload it to the root directory of your web app.
- Configure the
web.config(for IIS) or framework-specific error handling to redirect to this page.
By addressing these issues proactively, you can minimize disruptions and improve your site's usability.
Microsoft Azure Web App Error Page
When accessing a web application hosted on Microsoft Azure, you may occasionally encounter an error page. This page is displayed when the application fails to load due to technical issues. Understanding common causes and solutions can help resolve problems quickly.
Common Causes of Azure Web App Errors
- Application Crashes: The app may crash due to unhandled exceptions or runtime errors.
- Configuration Issues: Incorrect settings in app configuration files (e.g., web.config) can prevent proper execution.
- Resource Limitations: Exceeding CPU, memory, or bandwidth quotas may cause timeouts or failures.
- Deployment Problems: Incomplete or corrupted deployment files can lead to missing dependencies.
- Network Connectivity: Firewall rules or DNS misconfigurations may block access.
Troubleshooting Steps
If you encounter an Azure Web App error page, try these steps:
- Check the Azure Portal for service health notifications.
- Review application logs in the Azure App Service Logs section.
- Restart the web app through the Azure Portal.
- Verify connection strings and environment variables.
- Test with a basic "Hello World" page to isolate the issue.
Preventing Future Errors
To minimize disruptions:
- Implement proper error handling in your application code.
- Set up monitoring and alerts using Azure Application Insights.
- Perform staged deployments using deployment slots.
- Regularly test failover scenarios.
- Keep dependencies and frameworks updated.
For persistent issues, Microsoft provides detailed documentation and support options through the Azure portal. Remember that some errors may require investigation by your development team to identify application-specific problems.
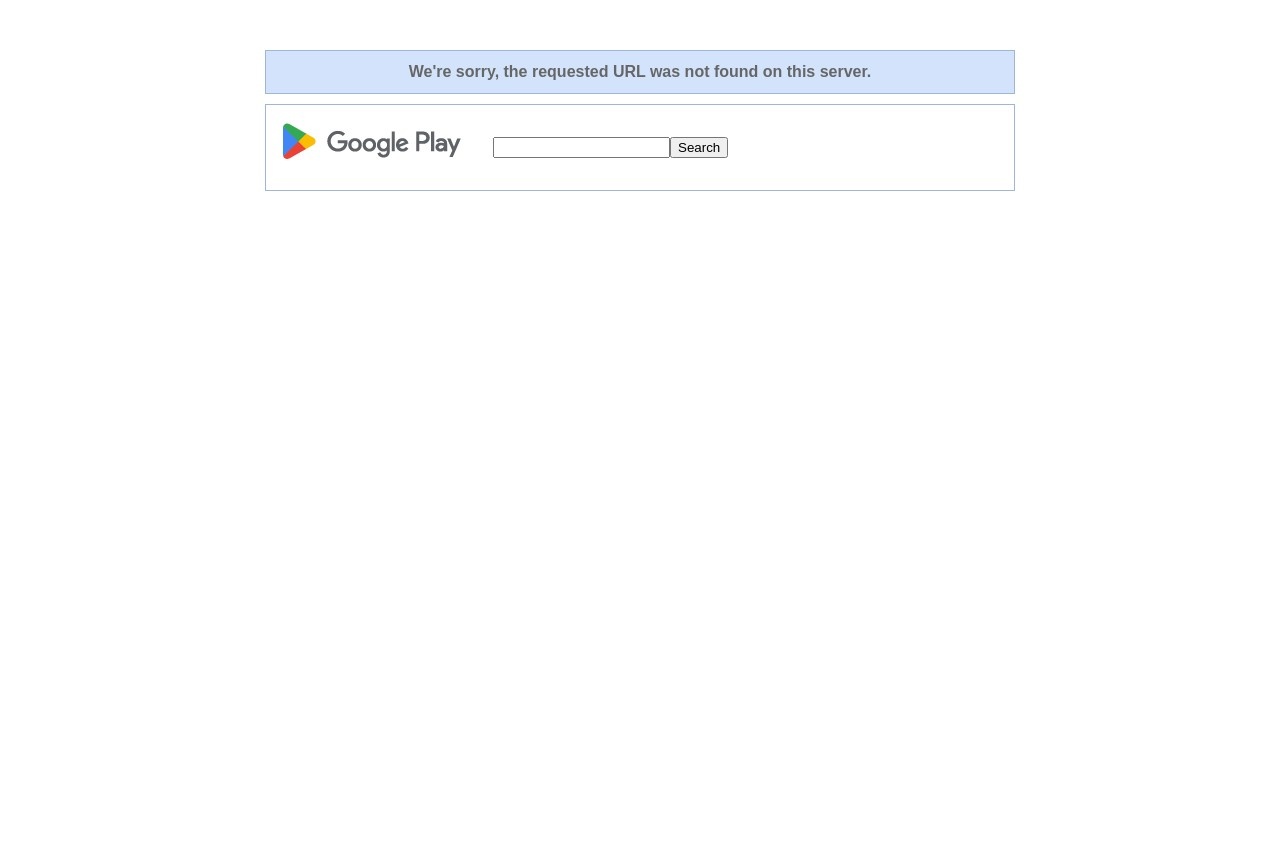
Microsoft Azure Web App 404 Error
When accessing a Microsoft Azure Web App, encountering a 404 error indicates that the requested resource could not be found. This issue may arise due to various reasons, ranging from incorrect configurations to missing files. Below, we outline common causes and troubleshooting steps.
Common Causes of 404 Errors
- Incorrect URL or Route: The requested path may not match any configured routes in the application.
- Missing Files: The web app may lack the necessary files (e.g., HTML, JavaScript, or images) at the specified location.
- Deployment Issues: The latest changes might not have been deployed correctly, or the deployment could be incomplete.
- Application Settings: Misconfigured settings, such as virtual directories or default documents, can lead to 404 errors.
- Authentication Requirements: If the resource requires authentication and the user is not logged in, a 404 may be returned instead of a 401 (Unauthorized).
Troubleshooting Steps
To resolve a 404 error in Azure Web Apps, follow these steps:
- Verify the URL: Double-check the URL for typos or incorrect paths.
- Check Deployment: Ensure the application files are correctly deployed to the expected directory.
- Review Application Logs: Use Azure App Service logs or application-specific logging to identify errors.
- Test Locally: Run the application locally to confirm the issue is not environment-specific.
- Inspect Azure Configuration: Validate settings like virtual directories, default documents, and authentication in the Azure portal.
- Restart the App: Sometimes, restarting the Web App can resolve temporary issues.
Preventing Future 404 Errors
To minimize 404 errors, consider the following best practices:
- Implement proper error handling to redirect users to a custom 404 page.
- Use automated testing to verify all routes and resources before deployment.
- Monitor application health using Azure Monitor or similar tools.
By understanding the root causes and applying these solutions, you can effectively address and prevent 404 errors in Microsoft Azure Web Apps.
Microsoft Azure Web App Error Page
When accessing a web application hosted on Microsoft Azure, you may occasionally encounter an error page. This page is displayed when the Azure Web App service encounters an issue preventing it from fulfilling your request. Understanding common error scenarios can help troubleshoot problems more efficiently.
Common Azure Web App Errors
- HTTP 403 Forbidden - Typically indicates permission issues or IP restrictions
- HTTP 404 Not Found - The requested resource doesn't exist or was moved
- HTTP 500 Internal Server Error - A generic server-side failure occurred
- HTTP 502 Bad Gateway - Often occurs during deployment or when the app crashes
- HTTP 503 Service Unavailable - The app may be undergoing maintenance or overloaded
Troubleshooting Steps
When you encounter an Azure Web App error page, consider these initial troubleshooting actions:
- Refresh the page after a few minutes - transient issues may resolve automatically
- Check the Azure Service Health dashboard for known outages
- Review your application logs in the Azure Portal
- Verify your application's configuration settings
- Ensure your subscription is active and payment methods are valid
Preventing Common Errors
To minimize Azure Web App errors, follow these best practices:
- Implement proper error handling in your application code
- Set up monitoring and alerts through Azure Monitor
- Use deployment slots for staging before production deployment
- Configure auto-scaling to handle traffic spikes
- Regularly test your application's failover capabilities
For persistent issues, Microsoft provides comprehensive documentation and support options through the Azure portal. Remember that many error conditions are temporary and can be resolved by the platform automatically.